Cloud Computing Introduction
1. Private Cloud
Dedicated data center for an organization hosted over internet.
2. Public Cloud
Public availability is a key difference between public and private clouds.
3. Hybrid Cloud
Users can flexibly choose which services to keep in public cloud and which to deploy to their private cloud infrastructure.
| Public Cloud | Private Cloud | Hybrid Cloud |
|---|---|---|
| No capital expenditures to scale up | Organizations have complete control over resources and security | Provides the most flexibility |
| Applications can be quickly provisioned and deprovisioned | Data is not collocated with other organizations’ data | Organizations determine where to run their applications |
| Organizations pay only for what they use | Hardware must be purchased for startup and maintenance | Organizations control security, compliance, or legal requirements |
| Organizations don’t have complete control over resources and security | Organizations are responsible for hardware maintenance and updates |
A fourth, and increasingly likely scenario is a multi-cloud scenario. In a multi-cloud scenario, you use multiple public cloud providers.
In Short
Key Characteristics
1. Scalability :
Vertical Scaling : CPU, Memory, Storage
Horizontal Scaling : instances of Resources or Nodes
2. Elasticity :
Ability to Scale Dynamically - Auto Scale feature
3, Agility
Ability to react quickly. (Ability to allocate and deallocate resources quickly)
In Cloud allocating resources might take time in seconds or minutes but on premises it might take days or weeks.
4. Fault Tolerance
Remain up and running during component and service failures.
5. Disaster Recovery
Disaster is a serious disruption of services caused by natural or human induces causes. Disaster recovery is the ability to recover from an event that has taken down the service. (Disaster).Achieved by replication.
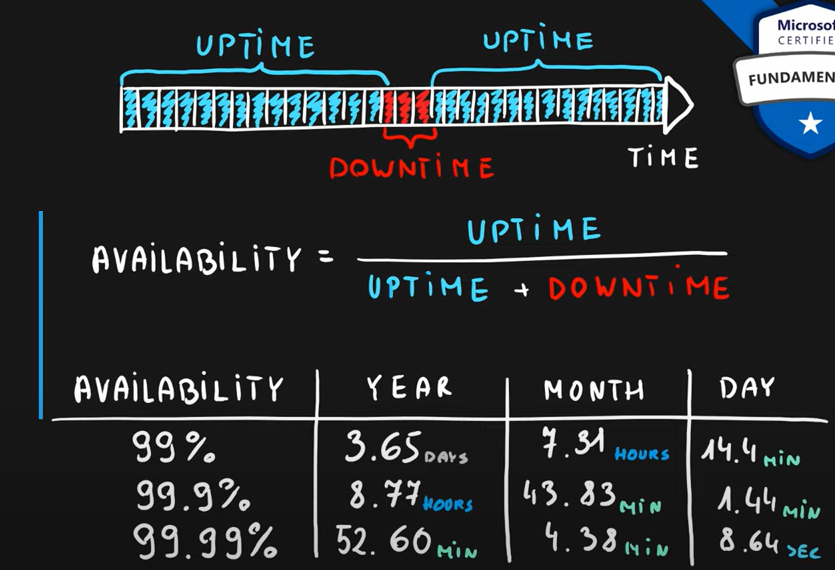
6. High Availability
Availability is a measure of system uptime for users / services. High availability is the ability to keep services running for extended periods of time with very little down time.
Consumption Based Model : When comparing IT infrastructure models, there are two types of expenses to consider. Capital expenditure (CapEx) and operational expenditure (OpEx).
In contrast, OpEx is spending money on services or products over time.
- No upfront costs.
- No need to purchase and manage costly infrastructure that users might not use to its fullest potential.
- The ability to pay for more resources when they're needed.
- The ability to stop paying for resources that are no longer needed.
Reference : https://marczak.io/az-900/#navigation
















No comments:
Post a Comment